Industry 4.0
Job Shop Scheduling
Job Shop Scheduling - automatic decision making according to data, conditions, hard and soft constraints, cost and time multi criteria optimization.
Example above: 16 working machines, 180 jobs, time 168 hours (1 week), several jobs connected, deadlines defined for all jobs except those connected, several machines (flashing red) excluded for certain interval of time. Cost and tardiness minimization
To come to the step that we have to solve the problem of Job Shop Scheduling (JSS), there are some processes that are included before, like decision which technology certain machine supports, the cost of operations, the probability of breakdown, can we do all the operations on the machine or we have to involve other machines in the chain, do we have enough material for operations on machine and the conditions of the material involved (temperature, humidity). And at the end, the delivery date (deadline) and we can plan even penalties for tardiness. (read more)
That`s all we have to think about to get the minimal production cost! No, we have to think about the crew and the knowledge they have, the interpersonal relationship and possible absence caused by illness! (read more)
All these things mentioned above influence to the process of optimization. So, if you want to cover all these things, we have to build a knowledge base. The JSS process inherits the knowledge base and according to logical model, decides how to optimize the problem. The times of simple Operation Research models are over.
Can we use the artificial intelligence? NO, in a classic way, learning by example! Why? We are looking for extreme (minimum or maximum), that`s why. Every optimization is unique, so how can we learn on the example bases. The technique of CDCL (Conflict Detection, Clause Learning) helps us to bound the decision tree whenever we calculate the optimization. But we can use the AI (learning by example) for searching the certain patterns in behaviour and control of the feedback data.
Example
Example above: 24 working machines, 220 jobs, time 168 hours (1 week), several jobs connected, deadlines defined for all jobs except those connected, several machines (flashing red) excluded for certain interval of time. Cost and tardiness minimization
For more examples, continue. How to combine Job Shop Scheduling with Shift Work?
Distributed Knowledge Base
We introduce CBB CmWell: an application for managing large volumes of linked data. “The focus of CBB CmWell is on content management and distribution: higher-level functions, such as reasoning, are left to other systems, but will be integrated in the next step”.
ClueBoomBus CmWell (CBB CmWell) is based on a clustered architecture (Fig. 1). The design of the solution consists of a well tested integration of a number of open source packages including CM-Well, Keycloak, Akka, Cassandra/FoudationDB, ElasticSearch, Jena, Shacl and Kafka.
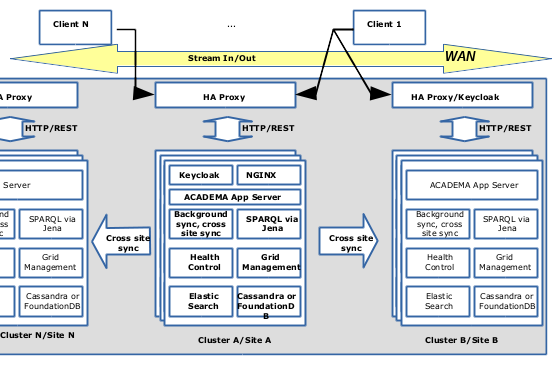
Fig. 1
Each node in the cluster has the same configuration and runs a set of processes with no single point of failure. Singleton control roles are moved between nodes on failure, implemented on a “self healing” principle. The majority of the application is written in the Scala language.
For more information, read article.
See also presentation.
Automated Guided Vehicles
Automated Guided Vehicles - automatic decision maker, according to data, conditions, hard and soft constraints, cost and time multi criteria optimization of planning, routing, etc..